- Home
- Sustainability
- Environment
- TCFD Scenario Analysis
TCFD Scenario Analysis
Climate Change Impacts on the Sumitomo Forestry Group (TCFD scenario analysis)
Regarding climate change, we examined the situation in 2030 based on two scenarios: a 4°C scenario where climate measures lag and a 1.5/2°C scenario reflecting progress toward decarbonization. We conducted an assessment of the financial impacts and discussed response measures for particularly significant risks and opportunities.
The results of our TCFD scenario analysis* conducted in 2018, 2021, and 2022, respectively, were reported to the Sustainability Committee and the Board of Directors each time and disclosed in the Sustainability Report and the Integrated Report. In addition, they are reflected as numerical targets for each division and department in the Mid-Term Management Plan "Mission TREEING 2030 Phase 2" (2025-2027).
*TCFD scenario analysis: We considered the situation in 2030 using two scenarios: the 4°C scenario, in which no further progress is made in tackling climate change, and the 1.5/2°C scenario, in which progress is made in transitioning the society toward decarbonization
| Setting scenario | 4°C scenario | 1.5/2°C scenario | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Assumptions on the societal status | A scenario where the status quo is maintained, economic development is prioritized, and global temperature rise and its effects continue to worsen | A scenario in which society as a whole takes a major turn toward decarbonization and succeeds in limiting temperature increases | |
| Reference scenario | For transition risks | Stated Policies Scenario (IEA) | Sustainable Development Scenario (IEA) Net Zero Emissions by 2050 (IEA) |
| For physical risks | SSP5-8.5 (IPCC) | SSP1-2.6 (IPCC) SP1-1.9 (IPCC) |
|
| Risks & opportunities | Physical risks and opportunities are likely to become apparent | Transition risks and opportunities are likely to become apparent | |
Source: Compiled from IPCC AR5, AR6, SR1.5, IEA WEO 2020, Net Zero Emission by 2050
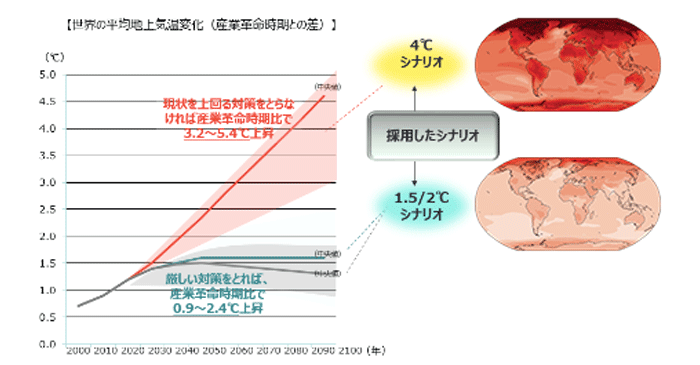
Source: Compiled from IPCC SR1.5 and AR6 WG1 SPM
- Click here for related information
Main Risks and Opportunities Identified
| Division*1 | Business | Transition Risks | Physical Risks | Opportunities | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Timber and Building Materials Business | Distribution and manufacturing of timber and building materials | C |
Cost increase due to introduction of carbon tax and stricter environmental regulations Increased wood procurement costs due to higher reforestation costs |
Decrease in value of wood and sales due to growing preference for more robust buildings as a result of more severe disasters |
Increase in demand for renovation to environmentally conscious housing due to stricter environmental regulations, and increase in sales of timber and building materials Increase in sales due to development of processing technology for materials for environmentally conscious housing and medium- to large-scale buildings |
| C ・ N |
Costs increase due to compliance with stricter laws and regulations related to illegal and unsustainable forest harvesting Costs increase due to higher wood procurement prices in response to increased demand for wood products to promote decarbonization, etc. |
Sales decrease and restoration costs increase due to severe flood damage from heavy rain and other factors or due to shutdown of operations Sales decrease and restoration costs increase due to suspension of operations following landslide in planted forests near plants Procurement costs increase due to reduced wood supply resulting from disasters and ecological degradation at procurement sites |
Sales increase owing to biorefinery technology and new product development Sales increase due to development of new products for the mass timber market Sales increase due to development of new products that contribute to the circular economy in the construction market |
||
| Housing Business | Custom-built houses, subdivision houses, greening (in Japan) |
C |
In the short term, technological development costs and construction costs for LCCM housing* and medium- to large-scale buildings will increase The value of wood will decline relatively over the long term due to the advancement of decarbonization technologies for steel, concrete, and other building materials, and sales of wooden buildings will decline |
Decrease in sales of timber and building materials due to growing preference for more robust buildings as a result of more severe disasters |
Increasing demand and sales of LCCM (Life-Cycle Carbon Minus) homes in response to growing decarbonization orientation Sales increase of environmentally conscious multi-family housing due to customer preferences, policy changes, etc. |
| C ・ N |
― |
Sales decrease due to construction delays caused by increased disaster risk Increased costs of premium payments to insurance companies due to increased disaster risk |
Sales increase due to sales at premium prices in conjunction by enhancing natural symbiotic functions (greening, water retention/permeable pavement, biodiversity initiatives, etc.) within housing and construction sites | ||
| Global Construction and Real Estate Business | Detached houses business (overseas), building materials manufacturing (United States), real estate development (Japan and overseas) | C |
Cost increase due to introduction of carbon tax and stricter environmental regulations Brand value loss due to delay in complying with environmental regulations, stock price slump, and sales decline |
Increased material procurement costs due to construction damage, extended construction time, and supply chain disruptions caused by severe disasters Intensifying competition to secure development sites due to a shift in demand to areas with less risk of disasters |
Increasing demand for environmentally conscious housing in response to the growing trend toward decarbonization among customers Expansion of the market for medium- to large-scale wooden constructions in response to ESG demand from investors and financial institutions |
| C ・ N |
Costs increase due to higher wood procurement prices in response to increased demand for wood products to promote decarbonization, etc. | Increased costs of insurance premium payments for properties under construction due to increased risk of natural disasters | Sales increase owing to the acquisition of new customers who value the natural environment following enhanced natural symbiotic functions (greening, water retention/permeable pavement, biodiversity initiatives, etc.) within housing and construction sites | ||
| Environment and Resources Business | Forest management, seedling production, and biomass power generation | C |
Decrease in wood production due to stricter forest protection policies Increased cost of installing energy-efficient heavy equipment due to the introduction of carbon taxes and stricter environmental regulations |
Increased forest road networks damage and road repair costs due to changes in precipitation and weather patterns Increased forest fires due to higher average temperatures, increased wood procurement and reforestation costs |
Increased demand for logs and wood due to customers' preference for decarbonization Increased demand for renewable energy due to strengthened decarbonization policies, and increased sales of biomass-derived energy business |
| C ・ N |
Costs increase due to compliance with stricter laws and regulations following the introduction of policies to promote certification of woody biomass feedstock and PKS Costs increase due to higher fuel costs resulting from increased demand and tougher competition for woody biomass feedstock and PKS Costs increase due to further changes in forest management practices to meet the growing demand for sustainable timber Costs increase due to delays in the introduction of efficient and advanced forestry technology |
Sales decrease due to shutdown of operations caused by forest fires or landslides | Sales increase from the generation of carbon credits in connection with the promotion of forest and peatland management and forest fund operations | ||
| Lifestyle Services Business | Nursing home operations and insurance business, etc. | C | Decrease in sales of gasoline card business due to shift from gasoline to electric vehicles |
Increase in costs for renovation of owned facilities and BCP response due to the severity of disasters Decrease in customers using owned facilities due to rising temperatures and increased costs for safety considerations |
Increase in insurance subscribers, shorter policy periods, more frequent renewals, and sales due to more severe disasters Increase in the number of Sumirin Denki subscribers due to customers' preference for renewable energy Customer acquisition by responding to customers' desire for decarbonization and for safety and security in the face of increasingly severe natural disasters |
(C): Items identified only through TCFD scenario analysis
(C/N): Items identified from both TCFD scenario analysis and analysis based on TNFD's LEAP approach
*1The Lifestyle Services Business underwent TCFD scenario analysis only
*2LCCM housing: houses that reduce CO2 emissions during construction, occupancy, and demolition, and also generate renewable energy using solar power generation, etc., to achieve negative CO2 emissions over their entire life cycle
Analysis of Financial Impacts
In terms of the TCFD scenario analysis, among the risks and opportunities identified through the business-by-business analysis, some are affecting more than one business, and the business and items experiencing significant financial impacts (the amount of impact is 10% or more of each division's operating profit) are presented below. The increasing operating costs associated with the introduction of the carbon tax, environmental regulations, and the intensification of weather-related disasters will affect Timber and Building Materials Business and all divisions, while the growing preferences of customers for decarbonization will present opportunities for Environment and Resources Business and all divisions.
| Factors | Factors of Particular Impact | Related Business | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Transition Risks | Policies and Regulations | Introduction of Carbon Pricing | [Risks]
Increase in business costs due to the introduction of carbon tax imposition and emission trading system (Timber and Building Materials, Environment and Resources) |
Timber and Building Materials, Housing, Global Construction and Real Estate, Environment and Resources, Lifestyle Services |
| Forest conservation policies | [Risks]
Increase in wood procurement costs due to payment of logging tax, logging fees, etc. (Timber and Building Materials, Environment and Resources) Increase in domestic wood costs due to the shift of reforestation costs as a result of mandatory reforestation, etc. (Timber and Building Materials) |
Timber and Building Materials, Environment and Resources | ||
| Introduction of environmental regulations |
[Risks]
[Opportunities]
Increase in sales due to increased demand for environmental certifications/low-carbon housing in response to stricter regulations on buildings (Global) |
Timber and Building Materials, Housing, Global Construction and Real Estate, Environment and Resources, Lifestyle Services | ||
| Market | Shift in customer orientation toward decarbonized products |
[Opportunities]
Increase in sales due to higher unit prices for logs and wood, associated with increased demand for renewable raw materials and products (Environment and Resources) |
Timber and Building Materials, Housing, Global Construction and Real Estate, Environment and Resources, Lifestyle Services | |
| Increased cost of raw materials | [Risks]
Increase in raw material costs due to higher energy costs (Timber and Building Materials) |
Timber and Building Materials, Housing, Global Construction and Real Estate | ||
| Technology | Advances in next-generation technologies |
[Risks]
Decrease in sales due to lower demand for wood as a result of progress in research and development of decarbonization of steel materials and concrete, which are competitors of wood (Timber and Building Materials) |
Timber and Building Materials, Housing, Global Construction and Real Estate, Environment and Resources | |
| Physical Risks | Acute | Intensifying weather disasters |
[Risks]
Cost increase due to higher purchase prices caused by supply chain damage (Global) |
Timber and Building Materials, Housing, Global Construction and Real Estate, Environment and Resources, Lifestyle Services |
Sumitomo Forestry's Countermeasures
In the TCFD scenario analysis conducted for all divisions from the end of 2022 to 2023, among the risks and opportunities identified in the business-by-business analysis, we identified items that affect multiple businesses. Of these, we identified particularly important items as cross-organizational issues, for which all divisions jointly discussed countermeasures.
Relationship Between Cross-organizational Issues/Countermeasures in TCFD Scenario Analysis and the Wood Cycle
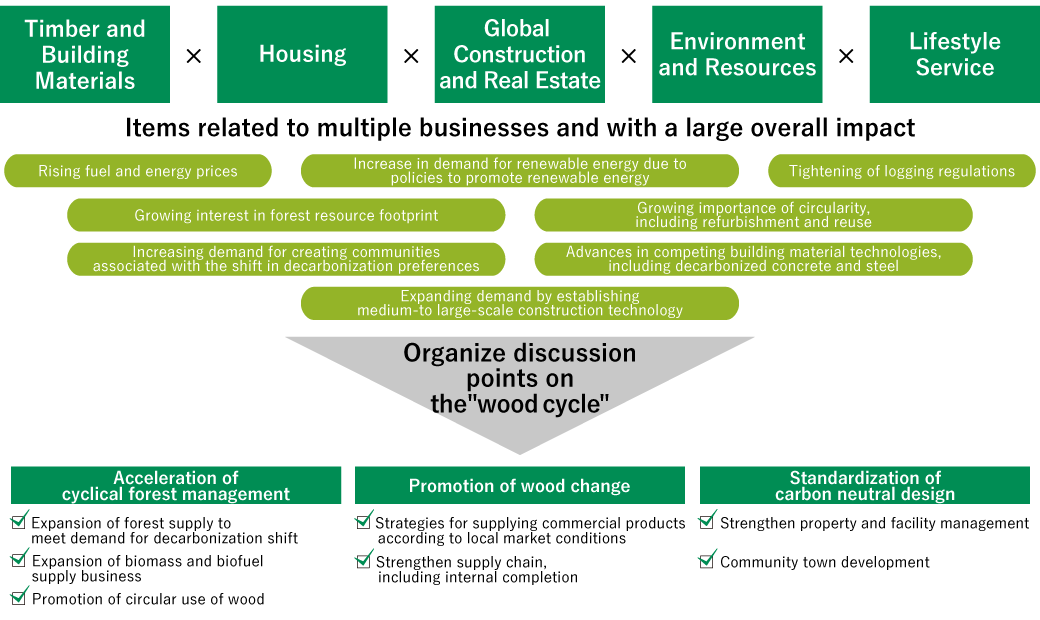
Proposed countermeasures identified through joint discussions with all divisions
| Items corresponding "wood cycle" | Cross-organizatioal issues | Countermeasures | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Energy | Forest | Expansion of forest supply to meet demand for decarbonization shift |
Development of tree species and forests in response to the decarbonization shift, such as fuel wood and high-strength wood Development of supply and demand for local production for local consumption (secure and consolidate mountain owners) |
| Wood | Expansion of biomass and biofuel supply business | Expand applications for wood chips and pellets that can be disposed of or used for biorefinery/SAF fuel by utilizing abundant forest resources and wood technology (considering development of wood-based SAF and challenging a demonstration plant) | |
| Materials | Wood | Strategies for supplying commercial products according to local market conditions | In order to standardize decarbonized design for medium- to large-scale buildings, on the basis of implementation and participation in planning activities, define the strategies of each region, select/cultivate company-owned forests, and develop commercial materials |
| Wood and Construction | Promotion of circular use of wood | New product design from the perspective of improving the scope and possibility of wood reuse at the time of demolition while lengthening the wood life cycle, and expanding the scope of reuse of demolition materials outside of the Kawasaki Chip Plant (biomass) | |
| Construction | Strengthen property and facility management | Expanding the stock-type business as building management to reduce GHG emissions after construction, from the viewpoint of building contracting | |
| Community townhouse development | Appeal from the perspective of environmental friendliness, in addition to the competitiveness of wood | ||
| Overall | Forest, Wood and Construction | Strengthen supply chain, including internal completion |
Upstream: the allocation of company-owned forests to be determined in consideration of the position of the forestry fund in the resource strategy, as well as supply chain efficiency Midstream: study and design the location and routing of production and distribution sites in accordance with upstream and downstream supply chain requirements Downstream: establish supply chain requirements by type of new construction, renovation/remodeling, etc., of houses, and coordinate with other departments |
- Home
- Sustainability
- Environment
- TCFD Scenario Analysis

